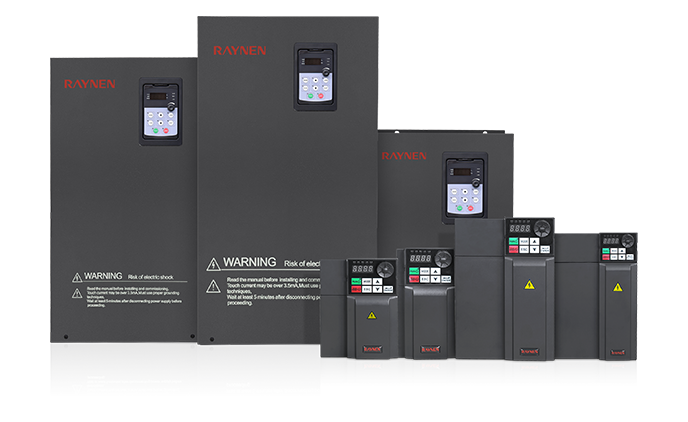
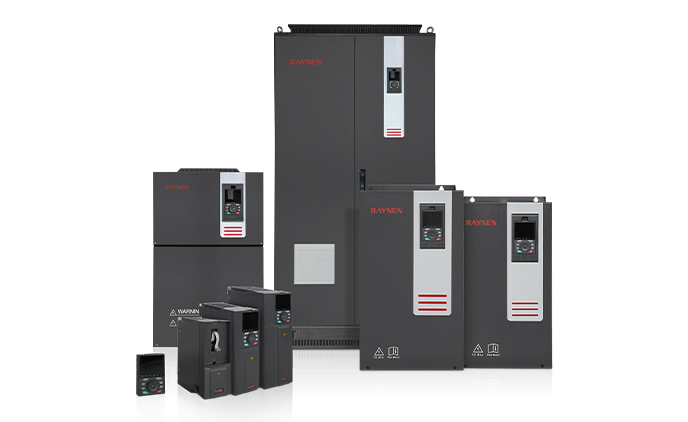
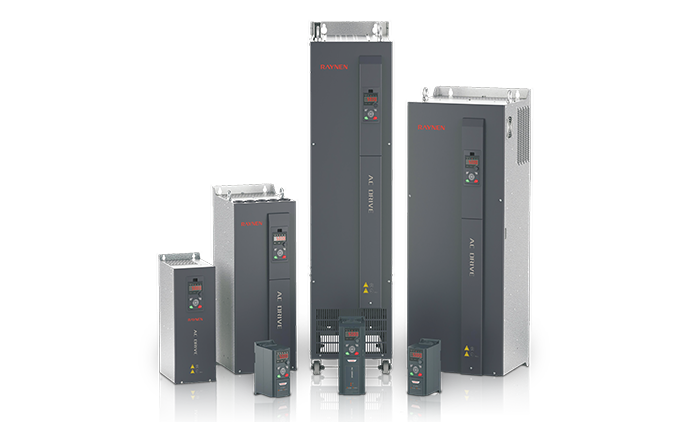
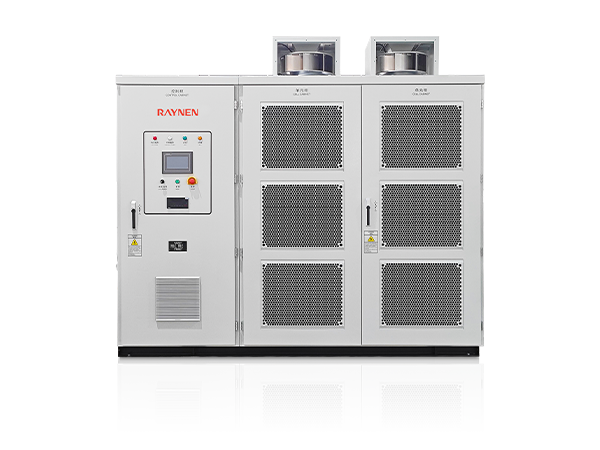
1.Introduction to AC Drives (Variable Frequency Drives) In the realm of modern industrial control an......
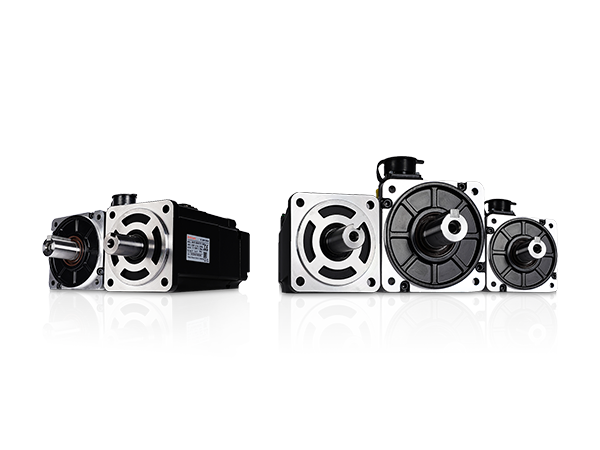
READ MOREHow to select the right industrial servo motor for my application?
1. Define Your Application Needs
First, you need to have a deep understanding of your application scenario. Ask yourself these questions:
-
Motion Type: Does your application require continuous rotation, reciprocating motion, or precise positioning? This will determine the requirements for speed, torque, and accuracy.
-
Load Characteristics: How heavy is the load that needs to be driven? Is the load inertial or constant? This directly impacts the required torque.
-
Duty Cycle: Will the motor operate continuously or intermittently? How long do the acceleration, constant speed, and deceleration phases last during a duty cycle? This determines the requirements for the motor's heat dissipation and overload capacity.
-
Environmental Conditions: In what kind of environment will the motor operate? Is there high temperature, high humidity, dust, or corrosive chemicals? These factors will influence the motor's ingress protection (IP) rating and material selection.
2. Core Technical Parameter Considerations
After gaining a clear understanding of your application, you can begin to evaluate the technical parameters of the servo motor.
a. Torque
Torque is the primary parameter when selecting a servo motor. It's categorized into three types:
-
Rated Torque: The torque the motor can continuously output at its rated speed. This is the torque you'll need under normal operating conditions.
-
Peak Torque: The maximum torque the motor can output for a short duration under overload. This is crucial for handling startup, acceleration, or sudden changes in load. Ensure the motor's peak torque meets the maximum instantaneous torque demand of your application.
-
Holding Torque: In some applications, such as those that require the motor to maintain its position after a power loss, holding torque is critical.
Torque Calculation: Accurate torque calculation needs to consider the load inertia, friction, gravity, and acceleration/deceleration torques. You can use professional software tools or formulas for this, and it's generally recommended to include a 20-30% safety margin.
b. Speed
Speed is also a critical factor. You need to know:
-
Rated Speed: The speed at which the motor can operate continuously and stably.
-
Maximum Speed: The highest speed the motor can achieve. Ensure this value meets your application's requirements, especially in scenarios that demand a fast response.
c. Inertia Matching
Inertia matching is one of the most easily overlooked, yet crucial, aspects of selecting a servo motor.
-
Theoretically, the optimal matching ratio is typically 1:1.
-
Practically, for rigid connections, the recommended ratio is usually between 3:1 and 5:1. For high-inertia loads, this ratio can be slightly higher, but an excessively high ratio (e.g., above 10:1) can make the system difficult to tune, cause vibrations, or even lead to instability.
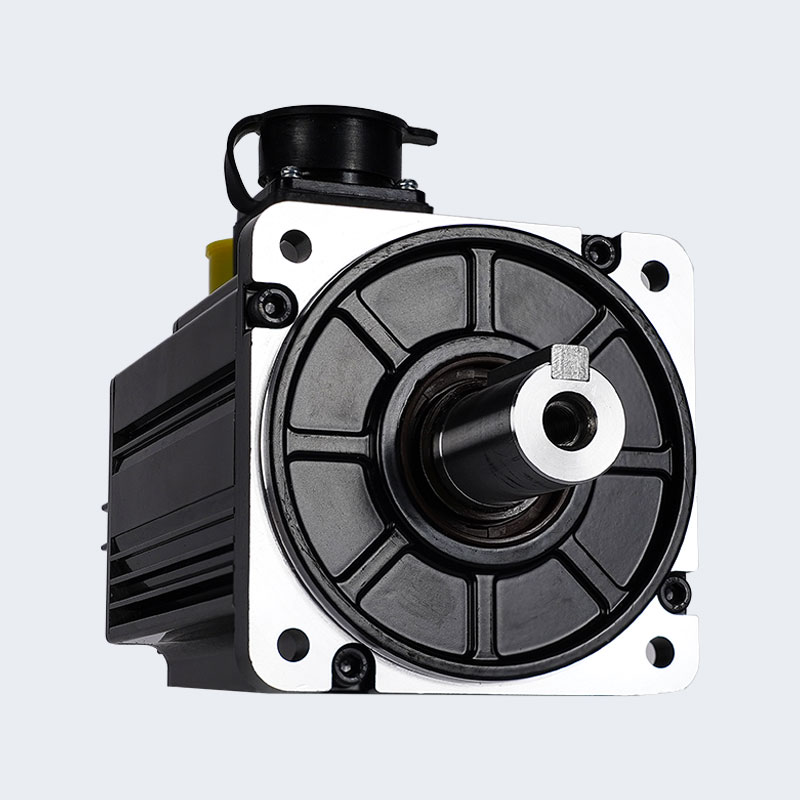

d. Feedback Device
The feedback device is at the heart of a servo system's precise control. Common types include:
-
Encoder: Provides position and speed information. Higher resolution leads to better positioning accuracy. Incremental and absolute encoders each have their pros and cons; the former is less expensive but requires re-homing after a power loss, while the latter does not.
-
Resolver: Performs more stably in harsh environments (high temperatures, vibrations) but typically has lower resolution than an encoder.
3. System Integration and Compatibility
Selecting a servo motor is not just about choosing the motor itself; it's also about considering its compatibility with the entire control system.
-
Servo Drive: Ensure the motor and the servo drive are compatible, ideally from the same brand or with certified compatibility. The drive needs to provide sufficient current and voltage to power the motor and support the required control modes (e.g., position, speed, or torque control).
-
Controller: Check if the servo motor and drive can communicate with your main controller (PLC, IPC, etc.). Common communication protocols include EtherCAT, Profinet, and CANopen.
-
IP Rating: Choose the appropriate IP rating based on your working environment. For example, IP65 or IP67 are typically used in dusty or wet environments.
Conclusion
Selecting the right industrial servo motor is a systematic process that requires a comprehensive evaluation of application needs, key technical parameters, and compatibility with the entire control system. We recommend collaborating with professional suppliers or engineers to use their expertise and technical support for accurate calculations and selection, ensuring your automated equipment operates efficiently and stably.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى