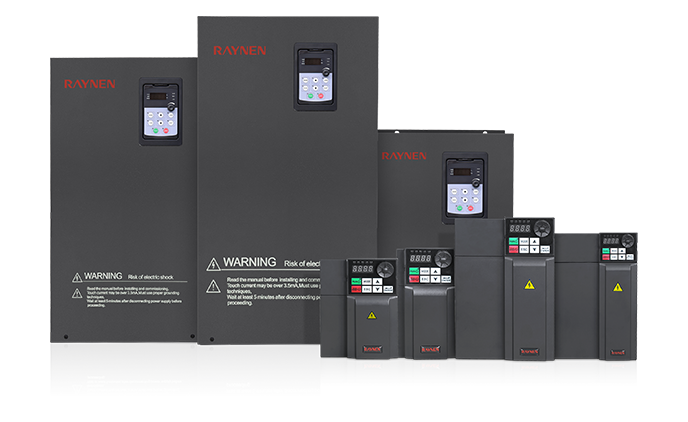
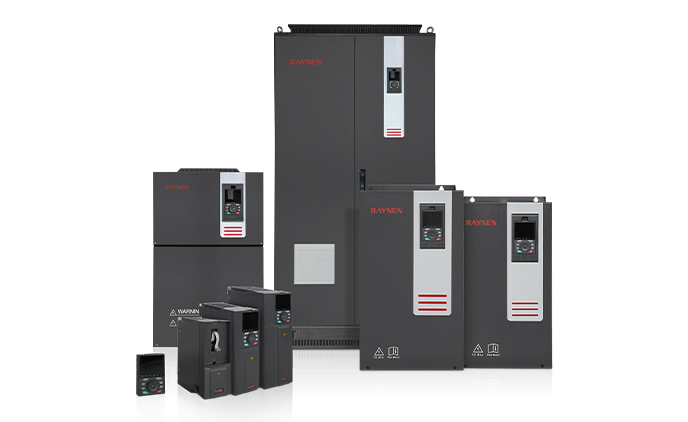
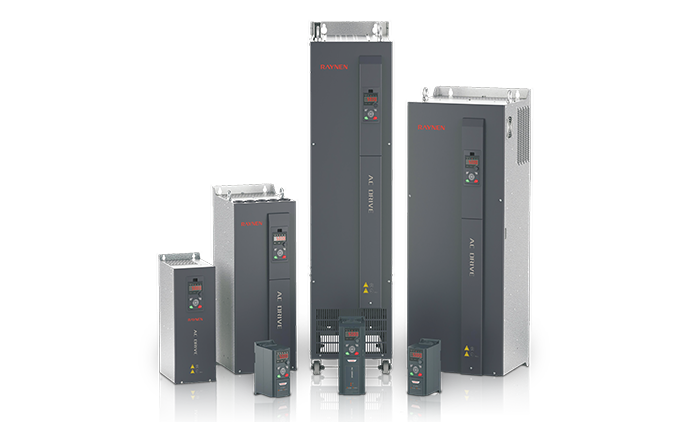
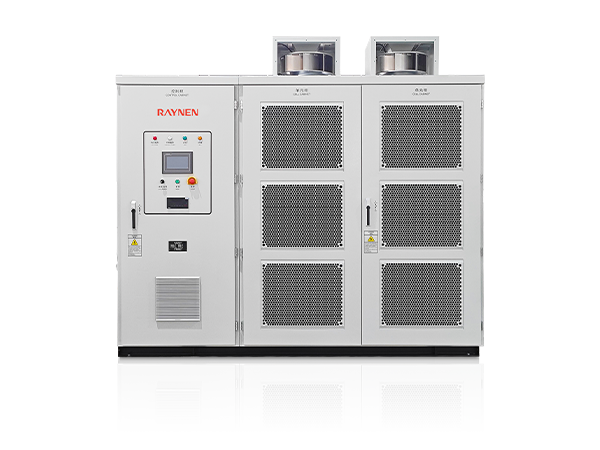
1.Introduction to AC Drives (Variable Frequency Drives) In the realm of modern industrial control an......
READ MOREWhat are common applications of industrial servo motors?
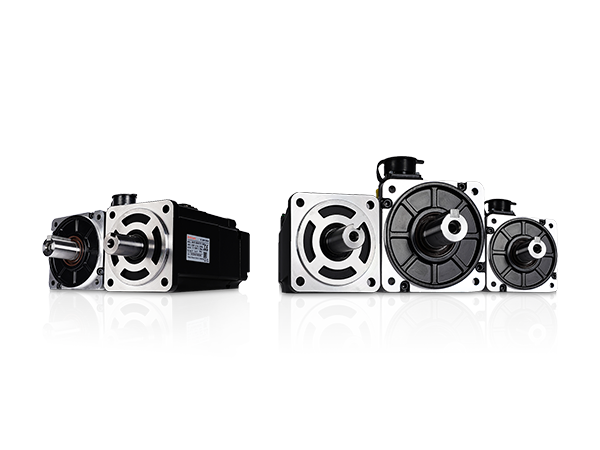
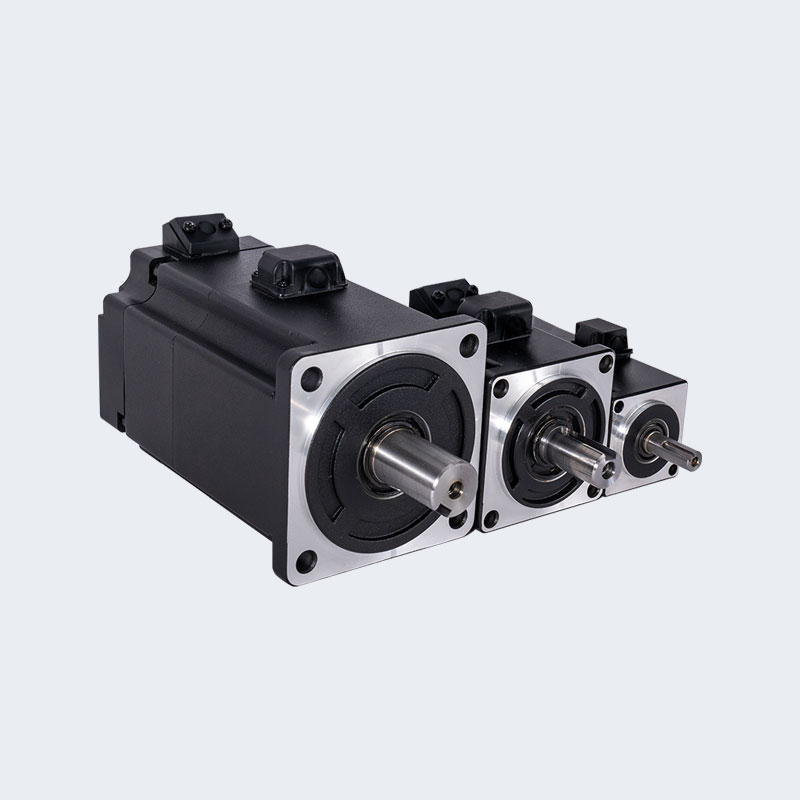
Industrial servo motors are a fundamental component in countless automated systems, known for their ability to deliver precise, high-speed, and high-torque motion control. Unlike traditional motors, a servo motor operates within a closed-loop system, constantly receiving feedback on its position, speed, and torque. This allows for unparalleled accuracy, making them the workhorse behind many of today's most sophisticated manufacturing processes.
High-Precision Positioning and Automation
One of the most common applications of a servo motor is in robotics. Industrial robots, from multi-axis articulated arms to SCARA robots, rely on servos to achieve the highly accurate and repeatable movements needed for tasks like welding, painting, and assembly. The precision of the servo motor ensures that each movement is executed flawlessly, which is critical for product quality and consistency.
Similarly, they are essential for CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines. Whether it's a mill, lathe, or router, the accuracy of the machining process depends on the precise movement of the cutting tool. The servo motor provides the rapid acceleration and deceleration and the exact positioning required to create intricate and complex parts with high tolerance.
Packaging and Material Handling
In the packaging industry, speed and synchronization are key. Servo motor systems are widely used in filling, capping, and labeling machines. Their ability to quickly start and stop with high accuracy allows for seamless product handling, ensuring that each bottle is filled to the correct level, each cap is applied perfectly, and each label is placed in the exact same spot. A servo motor also enables rapid changeovers between different product sizes, increasing production flexibility.
For material handling, servos are integral to conveyor systems, pick-and-place machines, and sorting systems. They can precisely control the speed and position of items on a conveyor, allowing for efficient sorting and stacking. The rapid response and accurate control provided by a servo motor prevent bottlenecks and improve the overall throughput of a production line.

Printing and Textile Industries
The printing industry demands incredible precision, especially in applications like high-speed digital printing and flexographic printing. A servo motor is used to control the movement of print heads and rollers, ensuring that the paper or substrate is perfectly aligned and that the ink is applied with pixel-level accuracy. This results in sharp, high-quality images and text, even at very high speeds.
In textile manufacturing, servos are used in a variety of machines, including looms, knitting machines, and cutting systems. A servo motor can precisely control the tension of the yarn and the movement of the needles or cutting blades, which is essential for producing uniform fabric and intricate patterns.
Medical and Scientific Equipment
Beyond traditional manufacturing, servo motor technology plays a vital role in medical and scientific fields. They are found in MRI machines, where they control the precise movement of the patient table, and in surgical robots, which require exceptionally smooth and accurate motion for delicate procedures. A servo motor is also a key component in laboratory automation systems and precision dispensing pumps, where precise control over small volumes of liquid is critical.
In all of these diverse applications, the core benefit remains the same: the ability of the servo motor to provide a level of control—in terms of position, speed, and torque—that is unmatched by other types of motors. This is what makes it an indispensable tool for engineers and manufacturers looking to achieve the highest levels of performance and automation.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى