1.Introduction to AC Drives (Variable Frequency Drives) In the realm of modern industrial control an......
READ MOREThe Silent Muscle: How the Industrial Servo Motor Powers Our Automated World
More Than Just a Motor: The Essence of Servo Control
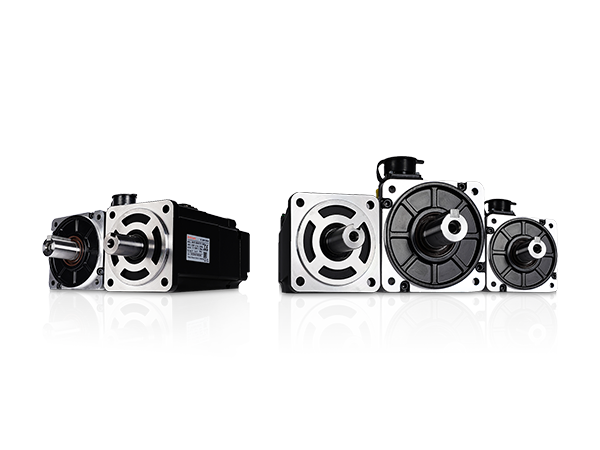
Have you ever watched a robotic arm in a car factory move with balletic precision, placing a part with millimeter accuracy? Or observed a high-speed bottling line that fills thousands of containers an hour without a spill? These feats of modern automation are made possible by a remarkable piece of technology: the Industrial Servo Motor.
Unlike a standard, everyday electric motor—like the one in a fan or a blender—which simply runs at a continuous speed, a servo motor is designed for precise control over its position, velocity, and acceleration. The word “servo” itself comes from the Latin word servus, meaning “slave,” which perfectly describes its function: it acts as a precise slave to a control signal, following instructions with incredible accuracy and responsiveness.
The Closed-Loop Secret: How a Servo Works
The core difference between a standard motor (an open-loop system) and a servo motor (a closed-loop system) lies in its ability to constantly check its work.
The Three Key Components
Every Industrial Servo Motor system relies on a trio of components to achieve its precision:
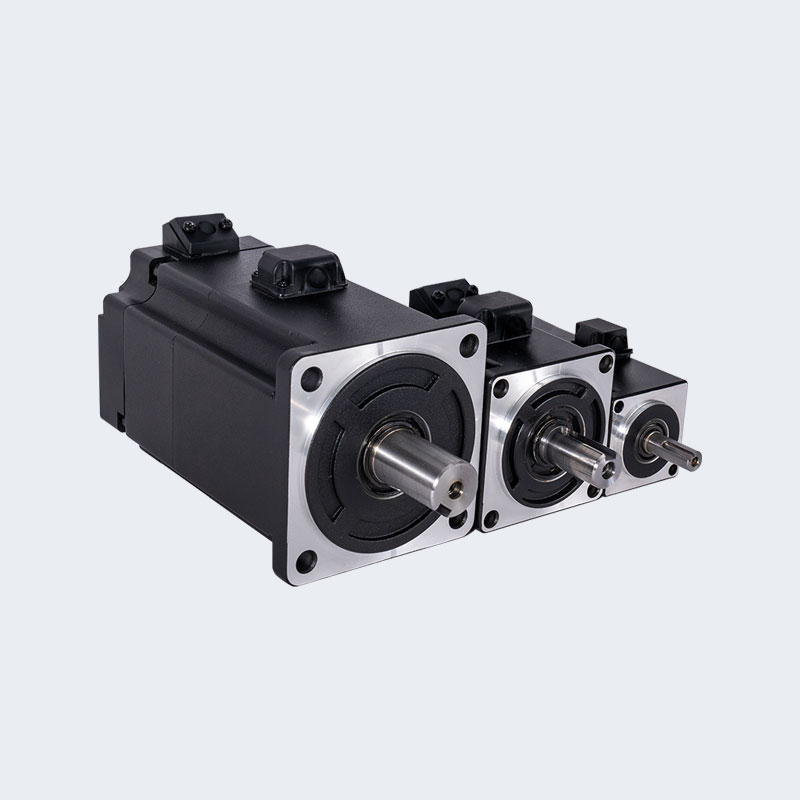
- The Motor (The Muscle): This is the device that actually produces the rotational force, or torque. In industrial applications, this is often a powerful AC or Brushless DC motor.
- The Feedback Device (The Eyes): This is typically a high-resolution encoder or resolver. It is mounted to the motor shaft and continuously measures the motor’s current position and speed. It acts as the “eyes,” sending real-time information back to the controller.
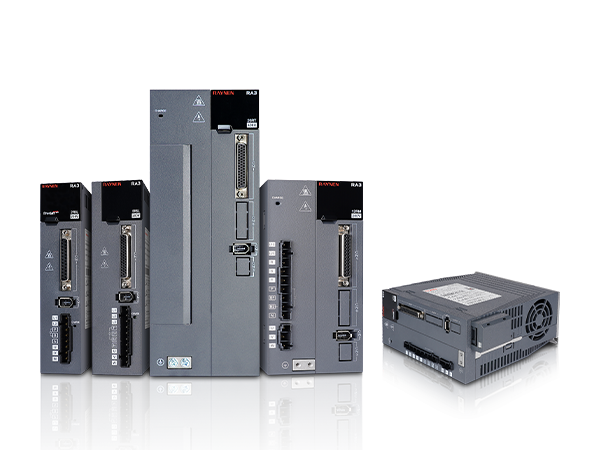
- The Servo Drive/Controller (The Brain): This electronic device receives the desired command (e.g., “move to 180 degrees”) and compares it to the actual position reported by the feedback device. If there is a difference (an “error signal”), the drive immediately adjusts the power sent to the motor until the actual position matches the commanded position. This constant comparison and correction is the essence of closed-loop control.
The Power of Precision
This closed-loop system gives the Industrial Servo Motor its superpowers. If an external force (a load) tries to push the motor out of position, the feedback device instantly senses the change, and the controller rapidly increases the motor’s torque to hold its ground, a capability known as high stiffness. This reliability and responsiveness are critical in environments where a slight error could ruin a product or cause a machine collision.
The Backbone of Industry 4.0
The applications of the Industrial Servo Motor are vast and fundamentally underpin modern manufacturing and automation. They are the driving force behind the global shift towards Industry 4.0—the push for “smart factories” where machines communicate and self-optimize.
Where Servos Live
- Robotics: They form the joints and actuators of industrial robotic arms, allowing them to perform complex tasks like welding, painting, and assembly with unmatched repeatability.
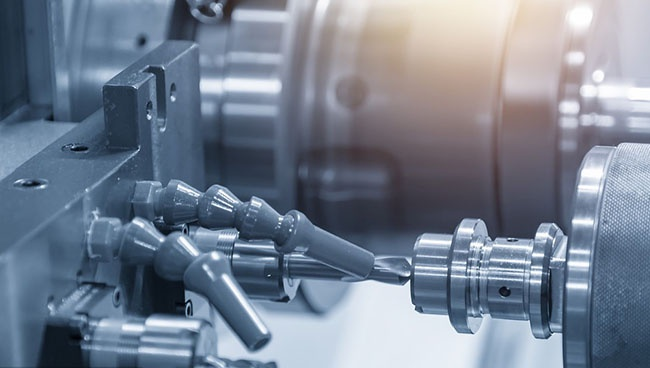
- CNC Machinery: In computer numerical control (CNC) machines, servos precisely control the movement of cutting tools and workpieces, ensuring micron-level accuracy in the fabrication of metal and plastic parts.
- Packaging and Bottling: They control the high-speed synchronization needed for filling, capping, and labeling lines, where motions must be coordinated in milliseconds.
- Printing and Converting: Servos maintain perfect tension and registration in printing presses and machinery that cuts, folds, or processes materials like paper, film, or textiles.
The future of the Industrial Servo Motor is evolving towards greater integration with technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Artificial Intelligence. Soon, these motors won’t just follow instructions; they’ll use their data to predict maintenance needs, optimize energy use, and even tune their own performance in real-time, making manufacturing processes even more efficient and autonomous.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى